Telsec Business Centers, an Alliance Virtual Offices member in Toronto, Canada, is known for being at the forefront of innovation, trends, and technology. One of the topics they’re experts in is SEO and how it can be used to increase website traffic. Recently, they shared with us an insightful piece on how to use one of the most important and free tools out there to improve website presence and traffic.
Below, you will find Telsec’s post on how to Increase Google Search Traffic by Using Google Search Console. You’ll find the post easy to read and follow; it provides detailed explanations and images to help you get going and advancing.
Written by Telsec
Google Search Console (GSC) used to be called Google Webmaster Tools, or GWT for short. The GSC is likely your best gauge of your site health in regards to the number of broken links to your site from other sites (always a good way to push those rankings higher), internal broken links, the indexability of your site, HTML “errors”, and the crawl rate which may be an indication of how much Google likes your content and much more. In this article I am going to go through the GSC and explain what your search console is telling you about your search engine visibility, the health of your site and how that information can be used to increase traffic. And if we are really lucky, we should be able to improve our page bounce rates and therefore conversion. I encourage those who have an SEO Agency doing this work for them to use this checklist and their GSC as a guide to accessing their performance.
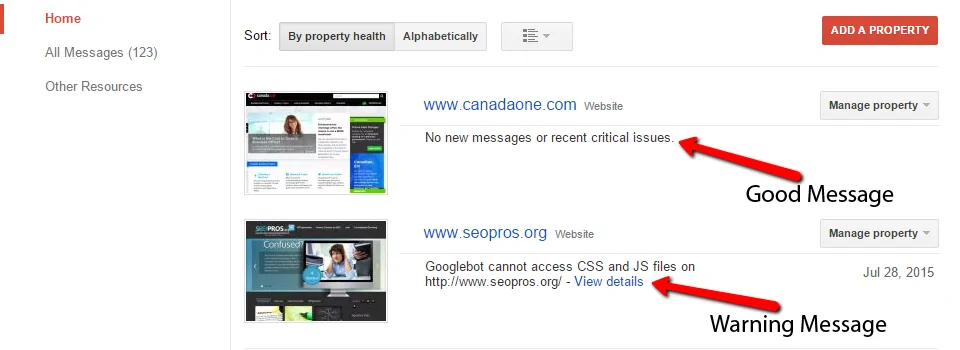
So let’s start our “magical mystery tour” of the GSC with the front page:
You’ll see I’ve put pointers to the important things on the entry page to GSC. The pointer labelled “good” shows a good site message while the “warning” pointer shows a warning for the Mobility update. These are both being re-developed in the near future partially because of the problems with the current responsive design not quite meeting Google standards, and it having been a few years since they were refreshed.
If you see this message you are definitely losing Mobile traffic and it could be affecting desktop rankings as well! This is not just about rankings (though this message is saying that Google has detected issues with the responsive design indicating that the site has issues with people using smartphones and to a lesser degree tablets).
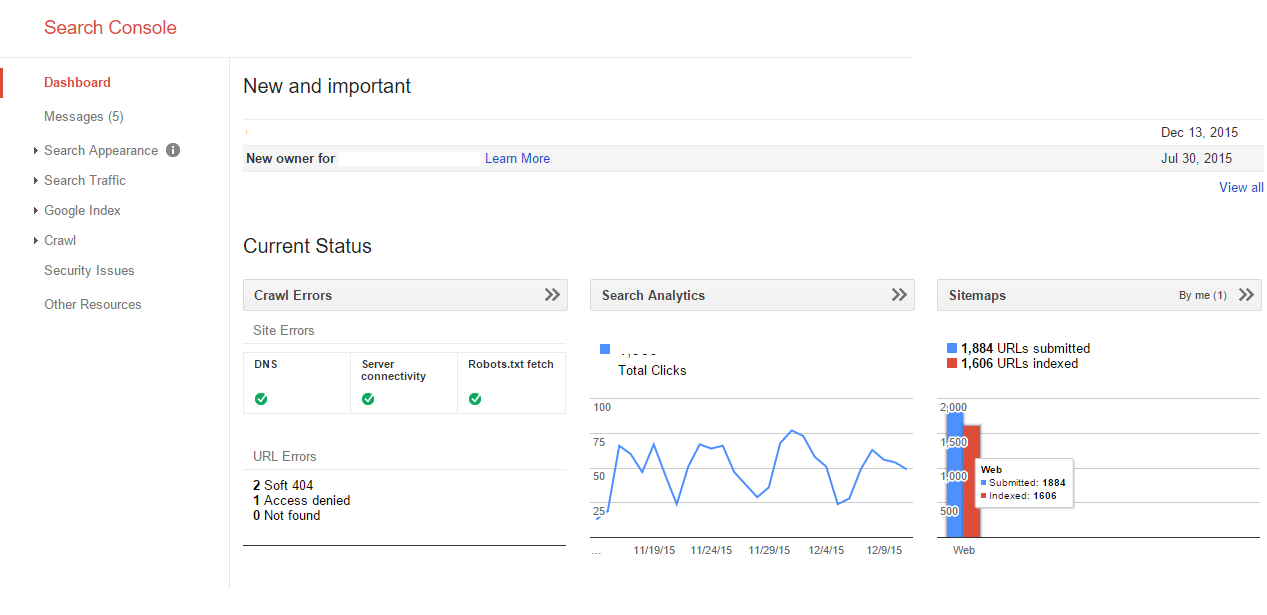
Current Status
Current status is another of the reports that indicates the general health of your website. The first box provides an overview of the “Crawl Errors”. The box next to that is your search analytics indicating information about rankings, impressions and CTR (Click Through Rate) on Google organic listings, and the third box contains an overview of your sitemap stats. The data in the three “Current Status Boxes” page are also located in other parts of the console; I will point them out when they are encountered and explain how I use the data to improve traffic or conversions.
Search Appearance
Search appearance is very important because this provides data on how your site is displayed in the SERP (Search Engine Results Page), and you can’t even begin to think of all the search terms that people would use to find your site and what was displayed in the listing. Rich snippets (rating stars, answer boxes, knowledge panels, etc.) will increase your Click Through Rate which will also help your rankings. So it’s a double win when you get a rich snippet – an important link included in your sitelinks which also drives more targeted traffic. Again, from strictly an SEO standpoint, finding ways to get an answer box or rich snippet is a huge achievement that will increase targeted traffic.
Structured Data
Structured data is used by Google to identify special information on a page like the type of business and location of your business centre. The main thing you want to see here is that there are no errors in your coding, and that the Organization and Place schema from schema.org are at the very least included on the home page. But my preference is to include these schema in every page because that associates the structured data with any other entities/topics on the page. Structured data is used to pull the information off a page for the rich snippets mentioned above and helps Google to disambiguate ambiguous addresses. Ambiguous addresses are a potential problem for a business centre where there are possibly hundreds or even thousands of businesses using the same address. The recent updates to Google’s local algorithm have raised speculation in the industry that Google has a definite preference for structured data to be used to indicate the business name, address, url and logo.
Data Highlighter
The data highlighter enables those not familiar with coding structured data to highlight data such as event listings, or review ratings on their site that this tool will build from the structured data for them. It doesn’t do all the schema you may want, but it’s a start. There are instructions here that show you how to do it.
HTML Improvements
This page calls these HTML improvements but it is better to think of them as errors. Pages with duplicate titles or meta descriptions may not appear in the Google index and therefore will not rank. You also lose control of which of these pages will be included for ranking purposes. These are easy fixes that may pose a problem to a website’s overall quality score. Google likes well thought out and maintained websites, so broken links or anything that causes the user experience or SERP to degrade in quality (poor titles and descriptions) are a drag on rankings.
Sitelinks
The most important item under the Search Appearance are the sitelinks that are included in a search for your company name. These are often very popular links accounting for large portions of traffic to most sites. The sitelinks are not listed here because this is just an informational page telling you how to remove links you do not think appropriate for your site, or pages that you think a user should not land on when coming to your site.
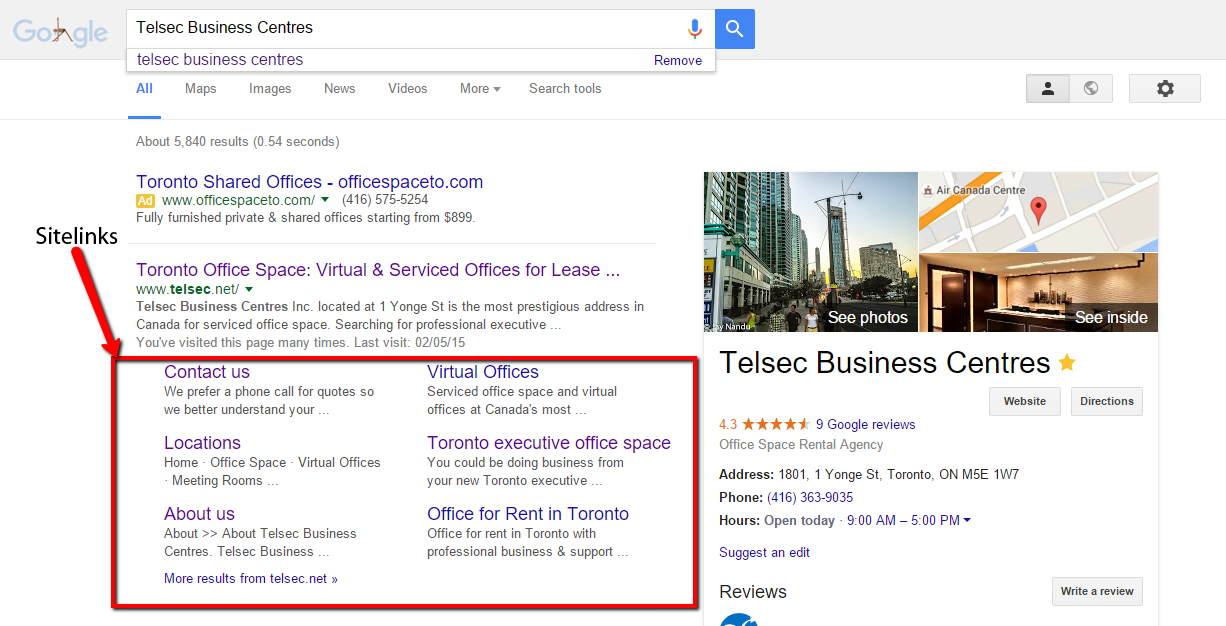
Sitelinks are the links below Telsec’s main page in the SERP pictured above. The easiest way to see your site links is to enter your business name into the Google search box. Note these are generally the pages on your website that get the most traffic and these sitelinks influence that. The best scenario is if you see pages to your primary services – such as office space and virtual offices – that they are among the links included in the sitelinks.
Search Traffic
Search Traffic is an important area because this is where you’ll find information on page impressions, clicks and average ranking positions; what Google knows about the links to/from and within your website, manual penalty information, where you target your international traffic, and where you test and review your mobile usability.
The links under “Search Traffic” can be used to identify why one page on your site may outrank your target page, internal links to your site that Google has discovered (it doesn’t always find them and needs a nudge in the right direction to do so), details on any manual actions and tools to target International traffic and test your mobile presence.
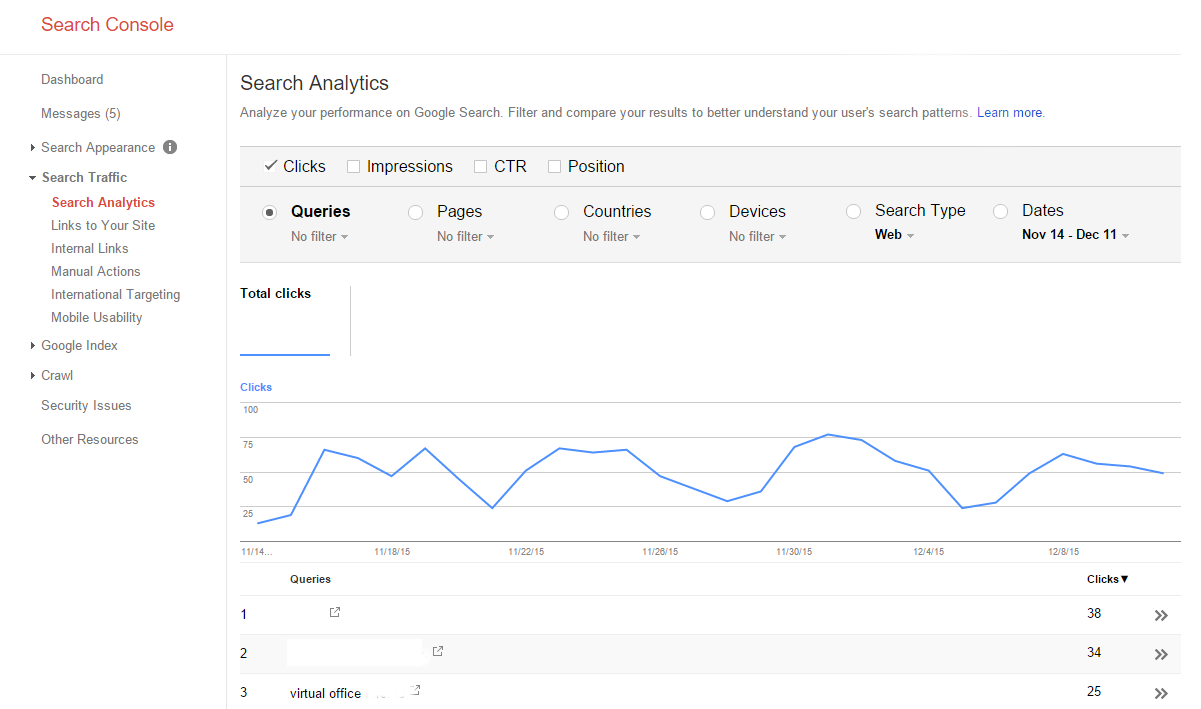
Search Analytics
I refer to this report as the “low hanging fruit report” because often I can find some excellent means to increasing traffic where the data shows me that making an improvement to some element of ranking should increase traffic.
This report includes clicks, impressions, CTR and average ranking position for all the keywords your site appears in the SERP. The first thing I do with this report is look for the keywords where the CTR (Click Through Rate) is low. Often by changing the title or adding a call to action like “One month’s free rent if you rent your office space today!” in the meta description or title. You should also find a lot of brand queries as leading keywords. Often these will return sitelinks that may vary from the obvious test which is the business name.
Links to Your Site
Links to your site is a very important element of how Google ranks pages in their results. For a business centre owner, the most important thing to make note of is that your office space and other service pages are at the top of the list. If they’re not, then the chances of those pages ranking above others on the site are diminished. One of the link patterns that has been identified as problem or could cause issues is when there are more links to internal pages than to the home page. I like to see a wide margin of difference between the number of links pointing at the home page versus all the other pages.
Internal Links
One thing you should look at here is that the pages that are the most important to your business (office space service pages, virtual office services page or boardrooms, etc.) are receiving more internal links than all other pages, because Google analyzes internal links to determine what you think is important on your site.
Manual Actions
Hopefully you never see anything here! The “Manual Actions” page will generally say “No manual webspam actions found.” If it doesn’t, then there will be more details about the manual action and the re-inclusion process.
International Targeting
Google uses hreflang tags to match the user’s language preference to the language variation you have chosen for your pages. If you’re using any hreflang tags on your site, you should see them here. In some cases, sites have had duplicate content and other issues arising from multiple language versions of the site being discovered by search engines.
Mobile Usability
I strongly suggest that this is another area of the GSC that business centre owners should check to make sure that their site is mobile friendly. Because if it’s not, then Google “may remove” these pages from the mobile results. I say may remove because it’s not always a given that you’re removed. But either way, this should be rectified so mobile users get a good experience while on your site!
Google Index
Items under the “Google Index” are generally pages with information about indexing of your site, keywords found in content, and pages where you have blocked indexing or asked to temporarily hide a page. Indexing of your site is important, so you may want to have a look at the pages in this section closely and in particular the “Content Keywords” report.
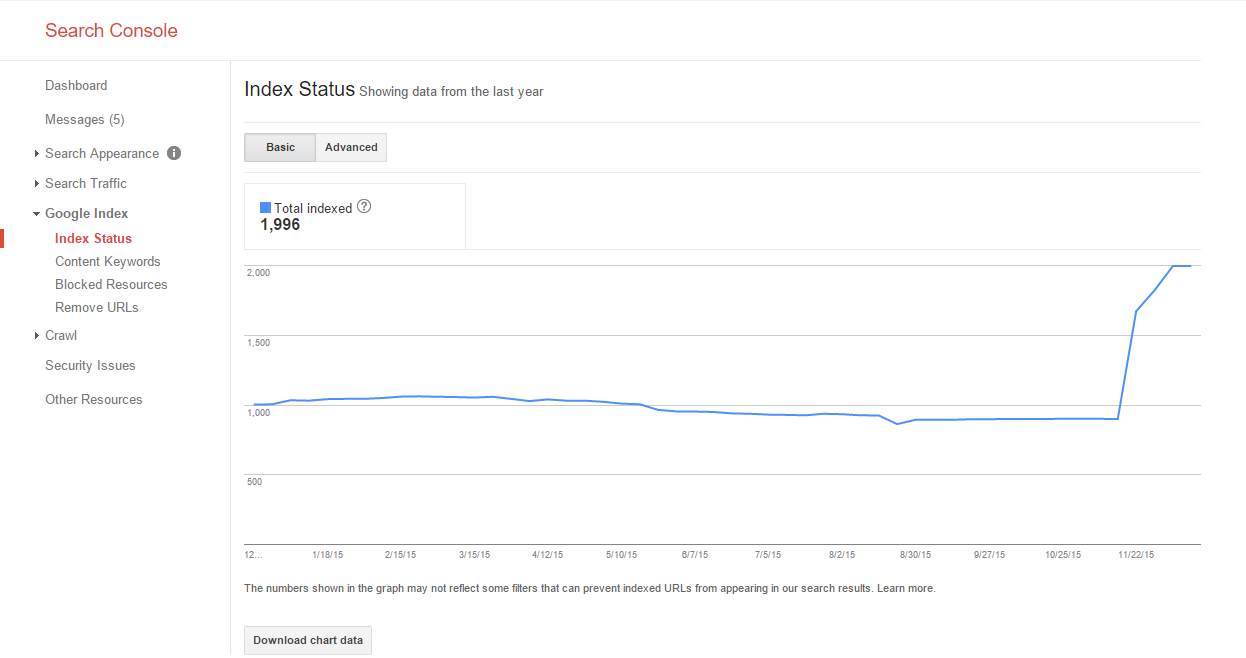
Index Status
This report tells you how many urls were indexed on your site. The timeline below the stats is important because it shows the trend in indexed urls – which in turn should always be rising unless you have removed content from the site.
Content Keywords
The “Content Keywords” is very important because again this is a report that indicates what Google thinks your site is about. It also indicates the significance of these words and how many variants it found on the site. The variants are important because the more you have, the more exact matches you have covered for ranking purposes. Variants could be co-occurrences which have become more important as Google becomes more reliant on linguistic semantics and the semantic web. Once again, for business centres, you want to see office, space, business, virtual etc. at the very top of the list with several variants.
Blocked Resources and Remove URLs
This reports any resources or URLs that your site is blocking or have requested to be removed from the index. If you see resources blocked in this report, I recommend that you use the “Fetch as Google” option. (I’ll explain the rest in that portion of the article).
If you see pages listed in the “Remove URLs” and you do not know about them, I strongly suggest you ask your webmaster or SEO about them, because often, pages are requested to be removed from the index when your website has been hacked/breached. As the owner or manager, you should be aware of any security issues. Generally, any information that’s requested to be removed from the Google index, you should be aware of the content and why it was removed.
Crawl
The “Crawl” group of reports provides statistics about how Google crawls/indexes a website and provides tools to test the files on your website that control how Google crawls your site, and errors it may encounter during the process. Errors could be in the robots.txt, broken links in a web page, misconfigured sitemaps, etc. So Google provides tools to test and see problems they are having indexing the site.
Crawl Errors
The Crawl Errors are so important that they are also included in the Current Status report, mentioned in any 404 (page not found) errors, and in soft 404’s, which are generally a case of a page sending a response code that Google does not believe to be valid. They’re often found where the server is misconfigured and sends a 200 “OK” response indicating a valid page was served when Google believes it should be a 404. These are the sorts of issues that end up costing you traffic because generally Google will not include these pages in the index. It also indicates the errors on different devices. Again, checking the “smartphones” and “feature phones” provides a different set of data that may indicate problems with your site on mobile devices.
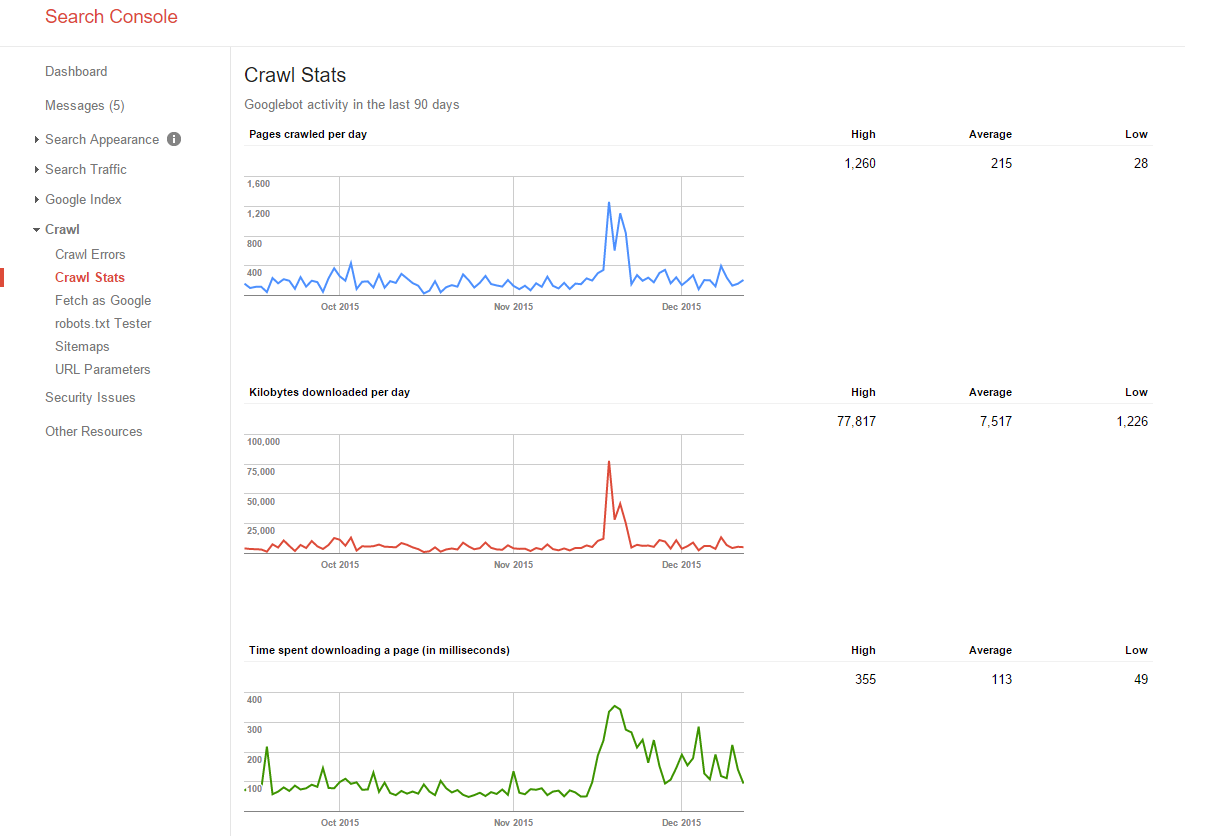
Crawl Stats
I don’t pay much attention to this one unless the timeline is going down from left to right which indicates Google is slowed the indexing of the site. This may mean there is a problem that needs to be addressed. I do pay special attention to the download times as that is a ranking factor, IMO, a small one and because anything that degrades the user experience is a problem that results in lower sales. Page-load speed is one of the things about a website that if the user doesn’t like it, you’ll definitely see sales affected negatively.
Fetch as Google
Above, I mentioned that I would go into more detail about this feature of the GSC. The first thing that I will point out is that all that follows assumes that the “Fetch and Render” option button was chosen. I often use this tool to and analyze what Google sees (and therefore can index) on a web page. If you recall, I mentioned that you wanted to use this if files were blocked on your website. A short time ago, Google announced that they no longer used the source code of the web page to index it. They are now going to use the rendered page as the medium for indexing. When you block resources on your website, it may block indexing of the element because Google is unable to see (render) it without the blocked resource. I also suggest that if your site has pages where important text is not displayed until you click a link or tab etc., then you may want to run those pages through the tool as well to see if the important text is seen by Googlebot.
robots.txt Tester
In this report, you can see the robots.txt file and test if specific URL’s are blocked by it. There are several ways to block resources. So if a URL is not in this report, it doesn’t mean that the blocked resources report is incorrect. It means it was likely blocked at the page level.
Sitemaps
This report tells you how many pages in the sitemap were submitted and indexed, as well as providing a way for you to test your sitemap and submit a fresh one.
URL Parameters
I strongly suggest if you don’t know what the title above refers to, that you move past this report without even reviewing it! 😉
Conclusion
The Search Console routine I’m discussing here is a result of coming to the “Sitemaps” page to refresh the sitemap on the last day of EVERY month. Yes, it is always the last day of the month so it always gets done on or about the same time (in case at some point we are analyzing the data) and mainly because I think this is so important that I do it every month. I hope you find this article useful in understanding how Google sees and ranks your website, as well as a few of the things you can monitor and better understand, and what your webmaster or SEO does and how to better evaluate the work being done for you.